Pavilion Publishing and Media Ltd
Blue Sky Offices Shoreham, 25 Cecil Pashley Way, Shoreham-by-Sea, West Sussex, BN43 5FF, UNITED KINGDOM
Commonly missed injuries
Part 2 of 2: Alistair Tindall FRCS, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, South London NHS Trust, answers more of your questions on traumatic injuries that are often overlooked or misdiagnosed in general practice.
How should Achilles rupture be treated?
Achilles rupture is often missed because, confusingly, patients may still be able to plantarex their ankle by using toe exor muscles or plantaris. The injury is most commonly a result of unaccustomed activity, especially tennis and squash.Patients may complain of a sudden, sharp calf pain, andexamination may reveal a gap at the musculo-tendinous junction,about 20cm above the heel.
Simmonds test should be part of the examination. If the test is positive, there is no movement of the foot on squeezing the corresponding calf, signifying likely rupture of the achilles tendon. Rupture of the medial head of gastrocnemius is a differential. Treatment consists either of surgical repair or immobilisation in plaster, with the toes pointing down to encourage the ends of the ruptured tendon to meet.
Achilles rupture increases the risk of DVT, as the pumping mechanism of the calf is disrupted. If missed, Achilles tendon rupture can lead to a weak, stiff ankle. Delayed presentation (>1 week) is a relative indication for surgery. Surgery is most successful within a couple of weeks of the injury, so referral to the fracture clinic is appropriate. Diagnosis can be confirmed on ultrasound.
What is a TFCC tear of the wrist?
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) of the wrist is akin to the meniscus in the knee. It sits just beyond the distal tip of the ulna. A tear is more common in the degenerate wrist and produces painful clicking over the ulnar side of the wrist joint. Rotation of the wrist joint in ulnar deviation can trap the torn fragment and provoke pain. Diagnosis therefore involves checking for painful clicking over the ulnar side of the wrist and for pain on rotating the wrist when it is in ulnar deviation. Wrist arthroscopy with TFCC repair is usually therapeutic.
What should we do about on-going symptoms in patients who have had an ankle sprain?

The anterior talo-fibularligament (ATFL) runs from thetip of the lateral malleolus to the talus. Pain resulting from a sprained ATFL is felt just anterior to the lateral malleolus. The ATFL is often injured as a result of an inversion injury, and in most instancessymptoms settle with physiotherapy, although this may take a few months. Persistent pain, tenderness or instability after a few months suggest ATFL rupture, and ATFL reconstruction should be considered, should symptoms warrant surgery.Diagnosis is with MRI.
What is the prognosis following a first episode of shoulder dislocation?
Within the young adult population, approximately a third of people make a full recovery following an anterior shoulder dislocation. Another third suffer from sequelae, such as instability; the final third become recurrent dislocators. Remember to check for nerve damage in the sergeant stripes territory of the axillary nerve (the patch of skin on the lateral aspect of the deltoid), as well as rarer but more serious brachial plexus injuries. Instability and recurrent dislocation are usually treated first by physiotherapy, but arthroscopic stabilisation is an increasingly common secondline treatment. In the elderly, persistent pain or weakness may arise from a tear of the rotator cuff, which occurred at the time of dislocation. An ultrasound is a quick, easy way of diagnosing this very treatable cause of persistent pain and weakness. Treatment may consist of a steroid injection or arthroscopic repair, but the choice of treatment is very complex and depends on many factors.
What is gamekeeper’s thumb? How should it be treated?
Gamekeeper’s thumb – also known as skier’s thumb – is the term applied to an injury of the ulnar collateral ligament (see figure). It is caused by a radial deforming force to the thumb, e.g. from a ski pole being knocked out of the hand, or coming to a sudden stop on a bike. Pain is felt over the ulnar aspect of the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint. A total rupture of the ligament often requires surgical repair, but the majority of injuries are sprains which can be managed conservatively with physiotherapy and analgesia. It is very difficult to differentiate between a sprained ulnar collateral ligament and a ruptured one on clinical examination alone, so if this injury is suspected, the patient should be referred. If untreated, a ruptured ulnar collateral ligament can lead to on-going pain and instability.
How does acromioclavicular joint disruption present?
Acromio-clavicular (AC) joint disruption can occur as a result of direct trauma to the tip of the acromion, e.g. falling and landing on the tip of the shoulder. Pain is felt over the AC joint, at the distal end of the clavicle. It results in reduced shoulder movement and a characteristic deformity, with prominence of the distal end of the clavicle. Most cases are treated nonsurgically with physiotherapy. However, surgical repair can be considered if there is a large deformity or if the patient is an overhead worker (such as a painter/decorator).
How do scaphoid fractures present?
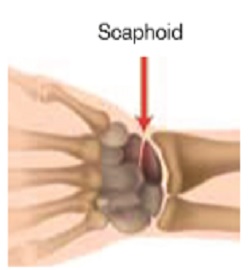
Scaphoid fractures are typically the result of a fall on an outstretched hand. On examination, there will be tenderness in the anatomical snuff box. X-rays need to include special scaphoid views, but even then are not very sensitive, especially in the first couple of weeks following injury. An MRI done acutely after the injury gives a definite diagnosis of fracture and can also help to rule out other injuries such as scapho-lunate ligament rupture. This is the imaging choice of most orthopedic surgeons for suspected scaphoid fracture, as it not only saves time in cast, but can also be cheaper overall than the traditional method of follow up in fracture clinic with delayed repeat x-ray. Missing a scaphoid fracture may result in non-union and subsequent collapse and degeneration of the wrist.


